Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
(1 point) A disturbance that transfers energy from
place to place is called a
a. | wave. | b. | medium. | c. | vibration. | d. | compression. |
|
|
|
2.
|
(1 point) Which is NOT part of the human eye?
a. | pupil | c. | optic nerve | b. | tapetum | d. | cornea |
|
|
|
3.
|
(1 point) Which best describes white light on the
electromagnetic spectrum?
a. | light that can not be seen | c. | ultraviolet
light | b. | visible light | d. | radio waves |
|
|
|
4.
|
(1 point) The amount of matter in an object is
called its
a. | inertia. | b. | mass. | c. | force. | d. | balance. |
|
|
|
5.
|
(1 point) The greater the mass of an object,
a. | the easier the object starts moving. | b. | the greater its inertia. | c. | the more balanced it
is. | d. | the more space it takes up. |
|
|
|
6.
|
(1 point) The ability to do work or cause change
describes
a. | density. | b. | energy. | c. | matter. | d. | temperature. |
|
|
|
7.
|
(1 point) When an object’s distance from
another object is changing,
a. | it is in motion. | b. | it is moving at constant
speed. | c. | it has a high velocity. | d. | it is
accelerating. |
|
|
|
8.
|
(1 point) Which example supports “Energy as a
funtion of motion?”
a. | radio waves | c. | a hot burner on a stove | b. | light
waves | d. | a
magnet |
|
|
|
9.
|
(1 point) Electromagnetic waves can transfer energy
without a(n)
a. | medium. | b. | electric field. | c. | magnetic
field. | d. | change in either a magnetic or an electric field. |
|
|
|
10.
|
(1 point) Which is an example of heat transfer by
conduction?
a. | Fire from a fire place | c. | heat from the sun | b. | touching a hot plate | d. | boiling water |
|
|
|
11.
|
(1 point) The force that one surface exerts on
another when the two rub against each other is called
a. | friction. | b. | acceleration. | c. | inertia. | d. | gravity. |
|
|
|
12.
|
(1 point) Which is not a simple machine?
a. | Pulley | c. | Wedge | b. | Axel | d. | Inertia |
|
|
|
13.
|
(1 point) What is required for a rocket to lift off
into space?
a. | thrust that is greater than Earth’s gravity | b. | mass that is greater
than Earth’s | c. | very little air resistance | d. | more velocity than
friction |
|
|
|
14.
|
(1 point) The force that pulls falling objects
toward Earth is called
a. | gravity. | b. | free fall. | c. | acceleration. | d. | air resistance. |
|
|
|
15.
|
(1 point) Which is an example of the transfer
of heat by convection?
a. | touching a hot burner | c. | electromagnetic waves | b. | pouring a cup of hot
water into a cold cup of water | d. | Mr. Scott shooting a rubber band at you. |
|
|
|
16.
|
(1 point) Balanced forces acting on an object
a. | always change the object’s motion. | b. | sometimes change the
object’s motion. | c. | never change the object’s
motion. | d. | are not related to motion. |
|
|
|
17.
|
(1 point) The law of universal gravitation states
that any two objects in the universe, without exception,
a. | attract each other. | b. | repel each other. | c. | combine to provide a
balanced force. | d. | create friction. |
|
|
|
18.
|
(1 point) According to Newton’s third law of
motion, when a hammer strikes and exerts force on a nail, the nail
a. | creates a friction with the hammer. | b. | disappears into the wood. | c. | exerts an equal
force back on the hammer. | d. | moves at a constant
speed. |
|
|
|
19.
|
(1 point) Which of the following is an example of a
simple machine.
a. | Pulley | c. | Bungy Chord | b. | Rope | d. | Mr. Howe’s
arms |
|
|
|
20.
|
(1 point) The momentum of an object is in the same
direction as its
a. | force. | b. | acceleration. | c. | velocity. | d. | inertia. |
|
|
|
21.
|
(1 point) The achievement of lifting a rocket off
the ground and into space can be explained by
a. | Newton’s first law. | b. | Newton’s second law. | c. | Newton’s third
law. | d. | the law of conservation of momentum. |
|
|
|
22.
|
(1 point) The tendency of an object to resist change
in its motion is known as
a. | mass. | b. | inertia. | c. | force. | d. | balance. |
|
|
|
23.
|
(1 point) The force of gravity on a person or object
on the surface of a planet is called
a. | mass. | b. | air resistance. | c. | weight. | d. | free fall. |
|
Completion
Complete each statement.
|
|
|
24.
|
(1 point) If the action force of a bat striking a
ball accelerates the ball in one direction, the reaction force accelerates the bat in the
____________________ direction.
|
|
|
25.
|
(1 point) A person traveling in a car that stops
suddenly keeps moving forward due to ____________________.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
26.
|
(1 point) DEFINE and EXPLAIN the difference between
Newton’s 1st & 2nd Law’s of Motion.
|
|
|
Use the diagram to answer each question. 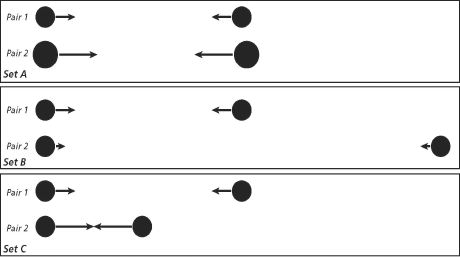 Assume that all of the objects in the diagram are solid and made of the same
material. Arrows represent gravitational force. Assume that all of the objects in the diagram are solid and made of the same
material. Arrows represent gravitational force.
|
|
|
27.
|
(1 point) In Set C, explain the difference in the
magnitudes of the gravitational forces between the two pairs of objects.
|
|
|
28.
|
(1 point) In Set A, is the gravitational force
greater between the objects in pair 1 or pair 2? Explain why.
|
|
|
29.
|
(1 point) In Set B, explain the difference in the
magnitudes of the gravitational forces between the two pairs of objects.
|
|
|
30.
|
(1 point) Compare the size and direction of the
gravitational force exerted by each object in pair 1 of Set A.
|
|
|
31.
|
(1 point) In Set A, what would you have to do to the
objects to make the gravitational forces between the objects in pair 2 the same as the forces between
the objects in pair 1?
|
|
|
32.
|
(1 point) Compare and contrast the differences and
similarities between heat and temperature.
|
|
|
33.
|
(1 point) Explain the relationship between inertia
and mass.
|
|
|
34.
|
(1 point) Explain how energy flows through a
medium.
|
|
|
35.
|
(1 point) What is the relationship between the Law
of Conservation and Newton’s 1st Law of Motion?
|
|
|
36.
|
(1 point) Describe the difference between contact
and action-at-a-distance forces.
|
|
|
37.
|
(1 point) What is energy?
|
|
|
38.
|
(1 point) What is Thermal Equilibreum?
|
|
|
39.
|
(1 point) What is heat?
|
|
|
40.
|
(1 point) Explain Newton’s 3rd law of
Motion.
|
|
|
41.
|
(1 point) In detail, explain the difference between
kinetic and potential energy.
|
Essay
|
|
|
42.
|
(1 point) You are sitting in a cold room and have
just started a fire in the fire place. Explain the process of how heat is being transfered from the
fire place to you. Include in your answer the type of heat transfer that is taking place, and the
flow of energy.
|
|
|
43.
|
(1 point) A book is sitting on the dashboard of a
car that is stopped at a traffic light. As the car starts to move forward, the book slides backward
off the dashboard. Use the term inertia to explain what happened.
|
|
|
44.
|
(1 point) Explain and give an example of
“Energy as a funtion of position”.
|
|
|
45.
|
(1 point) A bowling ball is attached to a rope and
the rope is tied to the ceiling. The bowling ball is then pulled back to a point and released. In
detail, explain how the following concepts are at work: Newton’s Law’s of Motion,
Inertia, Velocity, The Law of Concervation, and Kinetic vs. Potential Energy.
|
|
|
46.
|
(1 point) Explain and give an example of Radiative
Energy.
|
|
|
47.
|
(1 point) Explain and give an example of how
“Energy as a function of motion.
|